Amazon 1P vs. 3P: Which Selling Model Is Right for Your Business?
In the competitive world of e-commerce, Amazon offers two primary ways for businesses to sell their products: through a first-party (1P) or third-party (3P) relationship. Each model comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks, making it crucial for sellers to carefully evaluate which approach aligns best with the goals and size of their business, and desired level of control.
This guide explores the differences between Amazon’s 1P and 3P selling models, and provides a step-by-step approach to becoming a seller in either model while highlighting the pros and cons of each.
Table of contents
What is Amazon 1P (Vendor Central)?
In a first-party (1P) relationship, Amazon acts as the retailer, and you act as the supplier, selling your products directly to Amazon in bulk. This model operates through Vendor Central, a portal where vendors can manage their purchase orders (POs), view product details, and access advertising and reporting tools.
Pros of Amazon 1P:
Consistent purchase orders
Enhanced credibility
Streamlined fees
Advertising opportunities
Cons of Amazon 1P:
Loss of pricing control
Lower margins
Chargebacks
Dependence on Amazon
In conclusion, while the 1P model offers consistency and credibility, it also means ceding control over pricing and profit margins to Amazon, with potential risks tied to Amazon’s purchasing behavior and standards. This trade-off requires careful consideration of your business goals and long-term strategy.
What is Amazon 3P (Seller Central)?
In contrast, a third-party (3P) relationship gives you much greater control over your business. With the 3P model, you sell directly to customers via Amazon Seller Central, a platform where sellers manage their own product listings, pricing, and inventory. You also control how you fulfill orders—either through Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM), or Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP).
In this model, sellers are responsible for all of their own marketing, product detail page optimization, and promotional activities, but they also enjoy the flexibility of controlling their prices and brand presentation.
Pros of Amazon 3P:
Pricing authority
Brand control
Greater flexibility
Higher profit margins
Cons of Amazon 3P:
Time-consuming
Fees
Reputation management
In summary, the 3P model gives sellers control over pricing, branding, and product listings, offering higher profit potential and operational flexibility. However, it also entails managing everything from marketing to customer service, which demands significant time and attention. In contrast, the 1P model offers ease by handling logistics and customer service on your behalf, though it often comes with less control over pricing and lower margins.
Now we will elaborate on the pros and cons of each model in more detail so you can get a full picture of how they work.
What’s the Difference Between 1P and 3P?
Deciding between Amazon 1P and 3P depends on the size and goals of your business, and the level of control you want over your operations. Here are a few factors to consider:
Control Over Pricing
1P: Amazon controls product pricing, which can fluctuate based on its algorithm or pricing strategy.
3P: Sellers have complete authority over their prices, which allows them to be more competitive and react more quickly to market changes.
Brand Management
1P: Amazon may optimize your listings, so sellers lose significant control over how their brands are represented.
3P: Sellers have more hands-on control of their brand, including managing product detail pages and running custom marketing campaigns.
Fulfillment
1P: Amazon handles fulfillment after purchasing inventory from the sellers.
3P: Sellers can choose between fulfilling orders themselves (FBM) or using Amazon’s fulfillment services (FBA), which offers access to Prime members.
Profit Margins
1P: Vendors typically work with lower wholesale margins since they’re selling to Amazon.
3P: Sellers can enjoy higher retail margins by selling directly to customers.
By understanding the key differences between Amazon 1P vs. 3P, you can make a strategic decision that aligns with your business goals and helps you maximize your potential on Amazon’s vast marketplace.
Becoming a first-party seller can be pretty challenging, which is why it’s less common than the third-party route. So, let’s start by breaking down how to become a third-party seller, as this is a much simpler process.
How to Become a 3P Seller on Amazon: A Step-by-Step Guide
3P sellers are vendors who sell directly to consumers via Amazon's marketplace. The instructions are as simple as those needed to become an Amazon seller:
Step 1: Register for an Account
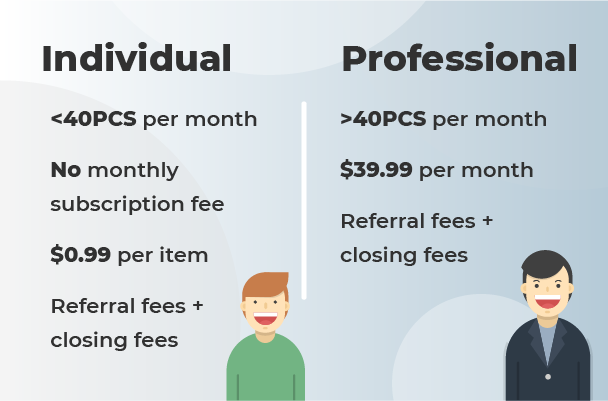
Sign up for an Amazon Seller Central account. This is your first step toward becoming a third-party seller. You’ll choose between an Individual or Professional plan, based on your selling needs.
Step 2: Check the Product’s Profitability
Before listing a product, ensure that it has high demand and offers a good profit margin. To find a profitable product, you can utilize special tools like the AMZScout PRO Extension to analyze market trends, competition, and potential profitability.
Here's how you can do that:
1. Install the AMZScout PRO Extension. There’s a free trial available—no credit card info is required.
2. Search for the product you’re interested in on Amazon. The tool will launch automatically and open its dashboard.
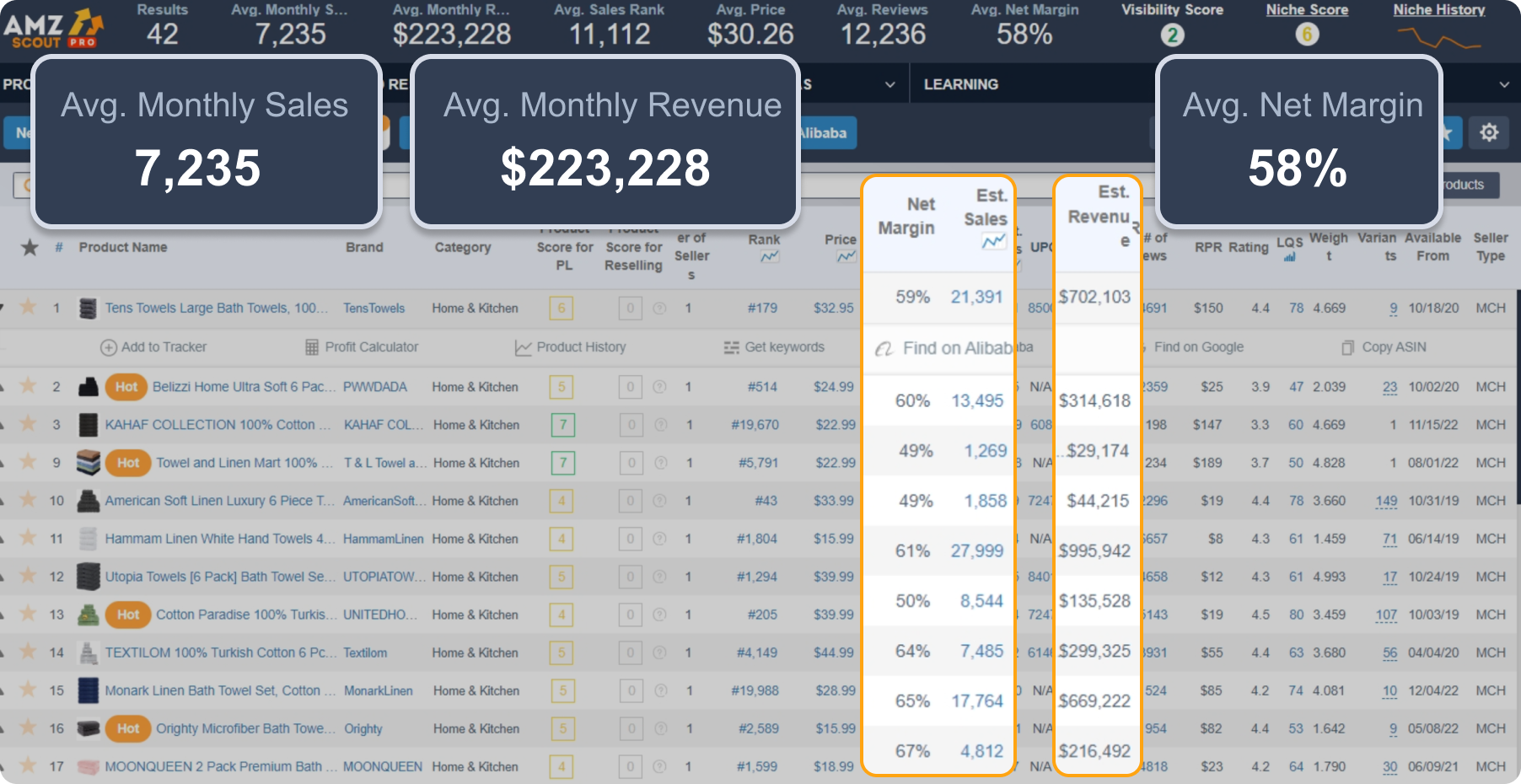
3. Review the key metrics. Now that you've opened the dashboard, it’s time to compare products within the niche to identify the most successful one. Focus on these crucial factors:
Monthly sales volume: Ensure that the product has strong demand by checking its monthly sales. Aim for consistent sales of over 300 units/month.
Evaluate the competition: Review the number of sellers on comparable listings if you’re a reseller. Ideally, aim for products with around 4–7 sellers, which suggests good resale potential without overcrowding. If you have a Private Label business, check out how many strong brands you’d need to compete with in the niche already.
Check the reviews: Make sure the product niche has solid customer feedback, with a rating of 4 stars or higher on average, which increases the likelihood of good sales.
4. Evaluate Profitability: Use the AMZScout Profit Calculator to assess the product’s profitability. After accounting for Amazon’s fees and shipping costs, the profit margin should remain strong. Look for margins of at least 20-30% to ensure that the product is worth selling.
By following these steps, you’ll get a deeper understanding of what your product is like. You will determine which selling strategy is best for it and take the reviews into consideration to help you understand how you can improve your product if needed.
Step 3: Find a Supplier
Once you’ve identified a profitable product, find a reliable supplier. You can source products through platforms like Alibaba or work directly with manufacturers. It’s also vital to choose your supplier thoroughly—you may opt to order just a small batch of the product for the first time to check the quality. If it’s alright, you may sign up for a continued collaboration.
Step 4: Create a Product Listing
Set up your product listing in Seller Central by writing compelling descriptions, titles, and bullet points. Use the AMZScout Keyword Search tool to find relevant keywords that will improve your listing’s visibility and help it rank higher among search results.
Step 5: Monitor Sales and Reviews
Track your sales and customer reviews regularly. Adjust your pricing, improve your listing, or update product features as needed to maintain high sales and positive feedback from buyers.
In conclusion, becoming a 3P seller on Amazon offers a great opportunity to reach a broad audience while maintaining control over your business. By using tools like AMZScout PRO to analyze market demand and profitability, you can set yourself up for long-term success in a highly competitive marketplace.
How to Become a 1P Seller on Amazon
To become a 1P seller on Amazon (also known as a vendor), you must first receive an invitation from Amazon. The platform selects brands and manufacturers based on product demand and performance.You can enhance your product visibility through Amazon’s advertising tools, like A+ Content and Amazon Marketing Services (AMS) to increase the likelihood that Amazon sees your product listing and sends you an invitation.
Once you’re invited, you’ll negotiate terms like wholesale pricing and shipping costs with Amazon. After finalizing the deal, you’ll register on Vendor Central, Amazon’s platform for managing purchase orders, shipments, and invoices.
As a 1P seller, Amazon buys your products at wholesale prices, takes control of pricing and inventory, and handles customer service and fulfillment. While you’ll lose some control over pricing and branding, you also gain access to Amazon’s extensive logistics and customer base.
Conclusion
Choosing the right selling model on Amazon is a crucial step in shaping your business’s future. Both selling models have their own benefits and major disadvantages, but it's important to assess which aligns best with your business. When deciding between becoming a 1P or 3P seller on Amazon, think about how much control you want over your brand. To grow your business while maintaining full ownership of your brand, consider using special tools like AMZScout for selling on Amazon, which can help you scale your business effectively.